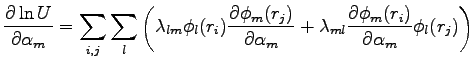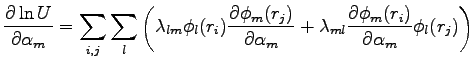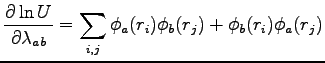Next: Derivatives of the local
Up: Three-body
Previous: Gradients and Laplacian
Contents
The derivative respect to a parameter 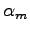 of an orbital
of an orbital 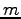 is given by:
is given by:
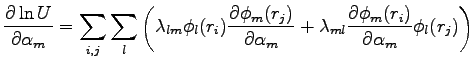 |
(B.29) |
and the derivative respect to
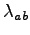 is
is
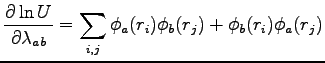 |
(B.30) |
because 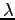 matrix is symmetric.
matrix is symmetric.
Claudio Attaccalite
2005-11-07